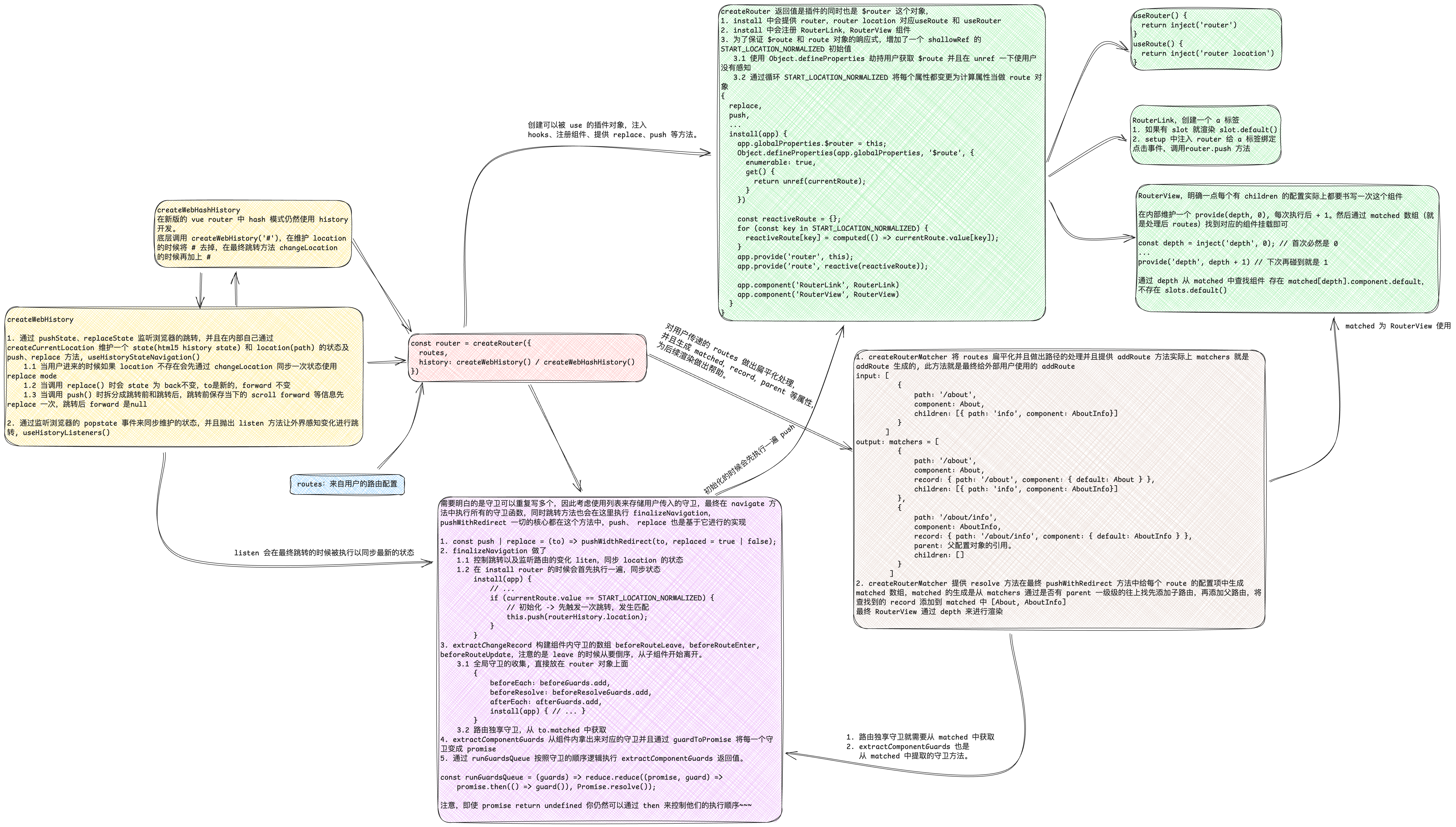
路由模式、路由创建、组件渲染、导航守卫实现
createWebHistory
该方法用于创建一个基于 HTML5 的 history 路由,内部使用 history.pushState 和 history.replaceState 来实现路由的跳转,并且会监听 popstate 事件来实现路由的回退。
在跳转的路由的同时会暴露出两个方法 push 和 replace 来实现路由的跳转。并且会在内部维护两个状态 currentLocation 当前路径和 historyState 当前状态。
/**
* 从 window.location 中获取 pathname、search、hash 并拼接成当前路径
* pathname 是 host 后面的路径
* search 是查询参数 querystring
*/
function createCurrentLocation() {
const { pathname, search, hash } = window.location;
return pathname + search + hash;
}
function buildState(back, current, forward, position, replaced = false, computedScroll = null) {
return {
back,
current,
forward,
position: window.history.length,
replaced,
scroll: computedScroll // 暂时不考虑计算滚动位置
}
}
/**
* 构建 historyState 及 currentLocation
* 暴露 push 和 replace 方法
*/
function useHistoryStateNavigation() {
const currentLocation = {
value: createCurrentLocation()
};
const historyState = {
value: window.history.state // 默认情况下是 null
}
// 当用户第一次来的时候,先同步一下状态
if (!historyState.value) {
changeLocation(
currentLocation.value,
{
back: null,
current: currentLocation.value,
forward: null,
position: window.history.length - 1, // length 默认从 2 开始,因为包含了 pushState 和 replaceState 两个方法
replaced: true,
scroll: null
},
true
);
}
/**
* 跳转并且更新状态
*/
function changeLocation(to, state, replace) {
window.history[replace ? 'replaceState' : 'pushState'](state, null, to);
historyState.value = state;
}
function replace(to, data) {
const state = Object.assign(
{},
window.history.state,
// 替换场景:back 是当前路径,to 是新的路径,forward 不变
buildState(historyState.value.back, to, historyState.value.forward, true),
data,
// 替换场景:position 无需更改
{ position: historyState.value.position }
);
changeLocation(to, state, true);
currentLocation.value = to;
}
function push(to, data) {
// push 之前需要考虑将当前页面下的 forward 和 scroll 保存
const currentState = Object.assign(
{},
historyState.value,
window.history.state,
{
forward: to,
scroll: null // 暂时不考虑计算滚动位置
}
);
// currentState.current 是当前路径 window.history.state.current
changeLocation(currentState.current, currentState, true);
// 保存成功之后做真正的 push
const state = Object.assign(
{},
// push 场景:back 是当前路径,to 是新的路径,forward 是 null
buildState(currentLocation.value, to, null, false),
{ position: currentState.position + 1 }, // 因为 push 之后,position 会加 1
data
);
changeLocation(to, state, false);
currentLocation.value = to;
}
return {
location: currentLocation,
state: historyState,
push,
replace
}
}
export function createWebHistory() {
const historyNavigation = useHistoryStateNavigation();
}目前来看已经可用了,但是浏览器的回退前进按钮是无效的,需要手动监听 popstate 事件来实现。
function useHistoryListeners(historyState, currentLocation, replace) {
let listeners = [];
const listen = (fn) => listeners.push(fn);
const popStateHandler = ({ state }) => {
// 跳转之后的路径
const to = createCurrentLocation();
// 当前位置
const from = currentLocation.value;
let isBack = false;
if (state) {
// 更新 currentLocation 和 historyState
currentLocation.value = to;
historyState.value = state;
// 大于 0 表示前进,小于 0 表示回退
isBack = state.position - historyState.value.position < 0;
}
listeners.forEach(fn => fn(to, from, { isBack }));
}
window.addEventListener('popstate', popStateHandler);
return { listen };
}
export function createWebHistory() {
const historyNavigation = useHistoryStateNavigation();
const historyListeners = useHistoryListeners(
historyNavigation.state,
historyNavigation.location,
historyNavigation.replace
);
const routerHistory = Object.assign({}, historyNavigation, historyListeners);
// 方便用户区域,做一层代理 xx.location 和 xx.state
Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'location', {
enumerable: true,
get() {
return historyNavigation.location.value;
}
});
Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'state', {
enumerable: true,
get() {
return historyNavigation.state.value;
}
});
return routerHistory;
}createWebHashHistory
在 Vue Router4 中,createWebHashHistory 和 createWebHistory 的实现方式是一样的,都是基于 HTML5 的 history 路由。
hash 路由的核心实现思想是,调用 createWebHistory 的时候传入 #, 处理 state 的时候将 # 去掉,真正跳转的时候,将 # 加上。
主要逻辑体现在 createCurrentLocation 和 changeLocation 中。
export function createWebHashHistory() {
// 获取当前路径
let base = location.pathname + location.search;
if (!base.includes('#')) {
base += '#';
}
createWebHistory(base);
}改造 createCurrentLocation,如果包含 hash 则返回 hash 后面的路径,否则返回完整路径。
function createCurrentLocation(base = '') {
const { pathname, search, hash } = window.location;
const hasPos = base.includes('#');
if (hasPos) {
return base.slice(1) || '/';
}
return pathname + search + hash;
}改造 changeLocation 跳转的时候把 # 加上。
function changeLocation(to, state, replace) {
// base 是透传进来的参数
const hasPos = base.indexOf('#');
const url = hasPos > -1 ? base + to : to;
window.history[replace ? 'replaceState' : 'pushState'](state, null, url);
historyState.value = state;
}createRouter
在工程化的脚本中,一切的开始都是从 createRouter。返回一个插件,最终将 router 挂载到 app 上。
可见在 createRouter 中,做了不少事情,工程中最常用的 RouterView RouterLink addRoute 路由钩子... 都是在这里实现的。
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import { createWebHistory, createRouter } from 'vue-router';
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About }
]
});
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app');本质上是根据一定的规则去渲染 routes 中的 component,需要一个匹配器去构建 routes 中的父子关系。在渲染的时候,从父到子,依次渲染。在卸载的时候,从子到父,依次卸载。
同时也要去构建 route router hooks ... 方法。
// 初始化路由系统中的默认参数 route 对象的初始化
const START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED = {
path: '/',
// params: {},
// query: {},
matched: [], // 当前路径匹配到的记录
}
/**
* options 使用户传入的配置
*/
export function createRouter(options) {
const matcher = createRouterMatcher(options.routes);
const routerHistory = options.history;
const currentRoute = shallowRef(START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED);
// 不考虑复杂的 to 类型,只考虑 string 类型
const resolve = (to) => typeof to === 'string' && matcher.resolve(to);
let ready = false;
function markAsReady() {
if (ready) return;
ready = true;
routerHistory.listen((to) => {
const targetLocation = resolve(to);
const from = currentRoute.value;
finalizeNavigation(targetLocation, from, true);
});
}
function finalizeNavigation(to, from, replaced = false) {
if (from === START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED || replaced) {
routerHistory.replace(to);
} else {
routerHistory.push(to);
}
currentRoute.value = to; // 更新 currentRoute;
// 加入监听
markAsReady();
}
/**
* 处理跳转
*/
function pushWithRedirect(to) {
const targetLocation = resolve(to);
const from = currentRoute.value;
finalizeNavigation(targetLocation, from);
}
const router = {
push: pushWithRedirect,
install(app) {
app.config.globalProperties.$router = this;
// 对于用户来说每次使用 $route 的时候要考虑 currentRoute 的变化同时要解构出来不可能让用通过 .value 去访问
Object.defineProperty(app.config.globalProperties, '$route', {
enumerable: true,
get() {
return unref(currentRoute);
}
});
const reactiveRoute = {};
for (const key in START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED) {
reactiveRoute[key] = computed(() => currentRoute.value[key]);
}
// useRouter 和 useRoute 的实现就是基于这两个 provide
app.provide('router', this);
app.provide('router location', reactive(reactiveRoute));
// import RouterView from RouterView.js / import RouterLink from RouterLink.js
app.component('RouterView', RouterView);
app.component('RouterLink', RouterLink);
// 初始化的时候先进行一次跳转
if (currentRoute.value == START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED) {
this.push(routerHistory.location);
}
}
}
return router;
}createRouterMatcher
createRouterMatcher 主要用于构建路由匹配器,构建父子关系,解析路径,并且拿到所有的组件方便后续渲染。
/**
* 构建标准的 route 对象
*/
function normalizeRouteRecord(route) {
return {
path: route.path,
name: route.name,
component: route.component,
children: route.children || []
}
}
/**
* 创建匹配记录,构建父子关系
*/
function createRouteRecordMatcher(normalizedRecord, parent) {
const matcher = {
path: normalizedRecord.path,
name: normalizedRecord.name,
record: normalizedRecord,
parent,
children: []
};
if (parent) {
parent.children.push(matcher);
}
return matcher;
}
function createRouterMatcher(routes) {
const matchers = [];
/**
* 该方法就是对外暴露 addRoute 方法
*/
function addRoute(route, parent) {
const normalizedRecord = normalizeRouteRecord(route);
if (parent) {
/**
* examples { path: '/home', children: [{ path: 'about' }] }
* result.path = '/home/about'
*/
normalizedRecord.path = parent.path + normalizedRecord.path;
}
const matcher = createRouteRecordMatcher(normalizedRecord, parent);
if ('children' in normalizedRecord) {
const children = normalizedRecord.children;
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
addRoute(children[i], matcher);
}
}
matchers.push(matcher);
}
/**
* 解析路径,并且拿到所有的组件方便后续渲染, 渲染时直接循环渲染即可。
*/
function resolve(location) {
const matched = [];
let matcher = matchers.find(m => m.path === location);
while (matcher) {
matched.unshift(matcher.record);
matcher = matcher.parent;
}
return {
path: location.path,
matched,
// [{path: '/home', component: Home}, {path: '/home/about', component: About}]
}
}
return { addRoute, resolve };
}RouterView 和 RouterLink
渲染一个 a 标签,点击的时候调用 router.push 方法。插槽使用 slots.default 方法。
const RouterLink = {
name: 'RouterLink',
props: {
to: {
type: String,
required: true
}
},
setup(props, { slots }) {
const router = inject('router');
return () => {
return h('a', { onClick: () => router.push(props.to) }, slots.default && slots.default());
}
}
};
export default RouterLink;const RouterView = {
name: 'RouterView',
setup(props, { slots }) {
const depth = inject('depth', 0);
const route = inject('route location');
const matchedRoute = computed(() => route.matched[depth]);
// 渲染嵌套路由的时候子组件中也要书写 RouterView 组件
// mathched 的结构是 [{path: '/home', component: Home}, {path: '/home/about', component: About}]
// 所以需要提供 depth 来区分是第几层
provide('depth', depth + 1);
return () => {
// setup 只会执行一次,所以需要使用 computed 来监听,在每次 render 的时候再获取一次最新的值
const matchRoute = matchedRoute.value;
const viewComponent = matchRoute && matchRotue.components.default;
if (!viewComponent) {
return slots.default && slots.default();
}
return h(viewComponent);
}
}
};
export default RouterView;useRouter 和 useRoute
本来不想写的,但是还是看看吧。
export const useRouter = () => inject('router');
export const useRoute = () => inject('route location');导航守卫
守卫分为三种形式,全局守卫,路由独享守卫,组件内守卫。对应路由的不同阶段的不同状态。详细
相同的钩子可以注册多个,所以考虑使用数组存储,做个简单的发布订阅。
改造 createRouter 中的 router 对象,添加导航 beforeEach、afterEach、beforeResolve 方法。对应全局前置、后置、解析守卫。
梳理调用链路得知,push -> finalizeNavigation -> 最终的 push,replace 方法。守卫基本上也就在 push 的过程中执行。为了保障执行的顺序通过 promise 链式调用。
const useCallback = () => {
const handlers = [];
const add = (fn) => handlers.push(fn);
// 提供一个只读访问,保证 handlers 的唯一性
return { add, list: () => handlers };
}
/**
* 提取出变化的路由记录
* beforeRouteEnter, beforeRouteUpdate, beforeRouteLeave
*/
function extractChangeRecord(to, from) {
const leavingRecords = [];
const enteringRecords = [];
const updatingRecords = [];
// 拿到最长的 matched 数组
const len = Math.max(to.matched.length, from.matched.length);
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const recordFrom = from.matched[i];
if (recordFrom) {
// 如果即在 to 中,也在 from 中,则认为是更新
if (to.matched.find(r => r.path === recordFrom.path)) {
updatingRecords.push(recordFrom);
} else {
// 如果不在 to 中,则认为是离开
leavingRecords.push(recordFrom);
}
}
const recordTo = to.matched[i];
if (recordTo) {
// 如果不在 from 中,则认为是进入
if (!from.matched.find(r => r.path === recordTo.path)) {
enteringRecords.push(recordTo);
}
}
}
return [leavingRecords, updatingRecords, enteringRecords];
}
function guardToPromise(guard, to, from, record) {
return new Promise((r) => {
const next = () => r();
// 执行用户传入的守卫
const fn = guard.call(record.component, to, from, next);
// 如果用户传入的是异步的守卫,则需要等待异步守卫执行完毕之后再执行 next
return Promise.resolve(fn).then(next);
});
}
/**
* 提取出组件内的守卫, 并且包装成 promise, 同时支持用户传入同步和异步的守卫, 也为了保证 next 的执行
*/
function extractComponentGuards(records, guardType, to, from) {
const guards = [];
for (const record of records) {
const rawComponent = record.component.default;
// 从组件的 options 中拿到对应的守卫
const guard = rawComponent[guardType];
// 包装成 promise
guard && guards.push(guardToPromise(guard, to, from, record));
}
return guards;
}
export function createRouter(options) {
const beforeGuards = useCallback();
const afterGuards = useCallback();
const beforeResolveGuards = useCallback();
// 将传入的数组中的每一项都包装成一个 promise,然后依次执行
const runGuardQueue = (fns) => fns.reduce((promise, fn) => promise.then(() => fn()), Promise.resolve());
function navigate(to, from) {
const [leavingRecords, updatingRecords, enteringRecords] = extractChangeRecord(to, from);
// 提取出离开的路由记录, 离开的时候从子组件开始
let guards = extractComponentGuards(leavingRecords.reverse(), 'beforeRouteLeave', to, from);
return runGuardQueue(guards)
.then(() => {
// 全局守卫 beforeEach
guards = [];
for (const guard of beforeGuards.list()) {
guards.push(guardToPromise(guard, to, from, guard));
}
runGuardQueue(guards);
})
.then(() => {
// 组件内守卫 beforeRouteUpdate
const guards = extractComponentGuards(updatingRecords, 'beforeRouteUpdate', to, from);
runGuardQueue(guards);
})
.then(() => {
// 路由独享守卫 beforeEnter
guards = [];
for (const record of to.matched) {
if (record.beforeEnter) {
guards.push(guardToPromise(record.beforeEnter, to, from, record));
}
}
runGuardQueue(guards);
})
.then(() => {
// 组件内守卫 beforeRouteEnter
const guards = extractComponentGuards(enteringRecords, 'beforeRouteEnter', to, from);
runGuardQueue(guards);
})
.then(() => {
// 全局解析守卫 beforeResolve
guards = [];
for (const guard of beforeResolveGuards.list()) {
guards.push(guardToPromise(guard, to, from, guard));
}
runGuardQueue(guards);
});
}
function pushWithRedirect(to) {
const targetLocation = resolve(to);
const from = currentRoute.value;
navigate(targetLocation, from)
.then(() => {
finalizeNavigation(targetLocation, from);
// 即使没有 return 也会把 undefined 包装成 promise
})
.then(() => {
// afterEach 全局后置守卫
for (const guard of afterGuards.list()) {
guard(to, from);
}
});
// 放弃原有的方案改用 promise 链式调用
// finalizeNavigation(targetLocation, from);
}
const router = {
// 最终都会通过 add 方法添加到 handlers 中,统一处理
beforeEach: beforeGuards.add,
afterEach: afterGuards.add,
beforeResolve: beforeResolveGuards.add,
// ...
}
return router;
}守卫的核心就是 navigate 方法。将 navigate 包装成 promise 方法支持链式的调用
- 在 finalizeNavigation 的下一个 then 中,执行 afterEach 全局后置守卫
- 通过 runGuardQueue 将钩子全部包装成 promise。
在 navigate 中执行组件内守卫 beforeRouteLeave -> 全局前置守卫 beforeEach -> 组件内守卫 beforeRouteUpdate -> 路由独享守卫 beforeEnter -> 组件内守卫 beforeRouteEnter -> 全局解析守卫 beforeResolve