Pinia 知识铺垫及简单 Demo
effectScope
创建一个 effect 作用域(实际上 setup 也算作一个作用域),可以捕获其中所创建的响应式副作用 (即计算属性和侦听器),这样捕获到的副作用可以一起处理。
function effectScope(detached?: boolean): EffectScope
interface EffectScope {
run<T>(fn: () => T): T | undefined // 如果作用域不活跃就为 undefined
stop(): void
}以 counter 功能为例;毫无疑问此时的 count 是响应式的。但如果增加一个停止功能使一些响应式结束,就需要使用 effectScope 对其改造一下。
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
const count = ref(0);
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2);
const tripeCount = computed(() => count.value * 3);
const onIncrement = () => count.value += 1;effectScope 会返回两个方法,run 和 stop 用于控制依赖的收集和停止;
import { ref, computed, effectScope, effect } from 'vue';
const scope = effectScope();
const count = ref(0);
let doubleCount = null;
let tripeCount = null;
scope.run(() => {
// 没有在文档中体现出来的方法,比较底层。执行时机与 watchEffect 类似
// 但是参数不一样;
// watch, watchEffect, effect 都基于 ReactiveEffect 实现。
effect(() => {
doubleCount = count.value * 2;
tripeCount = count.value * 3;
});
});
const onStop = () => scope.stop();
// ....还需要明白,stop 只会终止当前作用域中的副作用;假设把 tripeCount 抽离到另一个作用域中;此时的 stop 只会对 doubleCount 生效;
import { ref, computed, effectScope, effect } from 'vue';
const scope = effectScope();
const subScope = effectScope();
scope.run(() => {
effect(() => {
doubleCount = count.value * 2;
});
subScope.run(() => {
effect(() => {
tripeCount = count.value * 3;
});
});
});
scope.stop();如果换种方式,将 subScope 在 scope 中声明,则会被当做 scope 的作用域。此时可以通过参数来确定是否需要独立的作用域;
import { ref, computed, effectScope, effect } from 'vue';
const scope = effectScope();
const subScope = effectScope();
scope.run(() => {
const subScope = effectScope();
effect(() => {
doubleCount = count.value * 2;
});
subScope.run(() => {
effect(() => {
tripeCount = count.value * 3;
});
});
});
// 此时的 stop 会将两个 scope 全部停止;
// 但是 const subScope = effectScope(true) 时,
// subScope 就会重新开辟一个作用域,不再受 scope 的约束
scope.stop();Plugin (插件)
在 Vue 中插件的使用方式 app.use() 接受两个参数 app 和 options;
插件的实现方式有两种:
- 带有
install方法的对象 - 返回带有
install方法对象的方法。
需要知道是,app.use 的第二个参数会传给 install() 作为第二个参数;同一个插件多次注册,也只会被注册一次;
以 Counter 组件为例;常规的项目中,在使用时总是需要导入这个组件,并且使用;
// 在 setup 语法中只是需要导入,其他方式可能还要注册更加麻烦。
import Counter from './components/Counter.vue';解决以上问题的方式有很多,如果限定通过插件的方式呢?
// src/main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import counter from './plugins/counter';
const app = createApp(App);
app.use(counter(), { delay: 5000 });
app.mount('#app');
// src/plugins/counter.js
import Counter from '../components/Counter.vue';
export default function counter () {
return {
install (app, options) {
// app 即为整个应用的实例, 注册的组件也为全局组件
// 在此处将 Counter 组件注册。避免后续一直 import
app.component('Counter', Counter);
// { delay: 5000 }
console.log(options);
}
}
}当然了,install 的 app 不只是能注册组件,你可以在里面使用各种功能比如 provide mixin directive... 它是 Vue 的实例。
如果你想要把一些参数提前传递给 Counter 可以在注册组件时为其添加;
import Counter from '../components/Counter.vue'
export default function counter () {
return {
install (app, options) {
app.provide('delay', 2000);
app.component(
'Counter',
{
...Counter,
props: { delay: { type: Number, default: options.delay } }
}
);
}
}
}Pinia Demo
下载并注册插件
pnpm add piniaimport App from './App.vue';
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import { createPinia } from 'pinia';
createApp(App)
.use(createPinia())
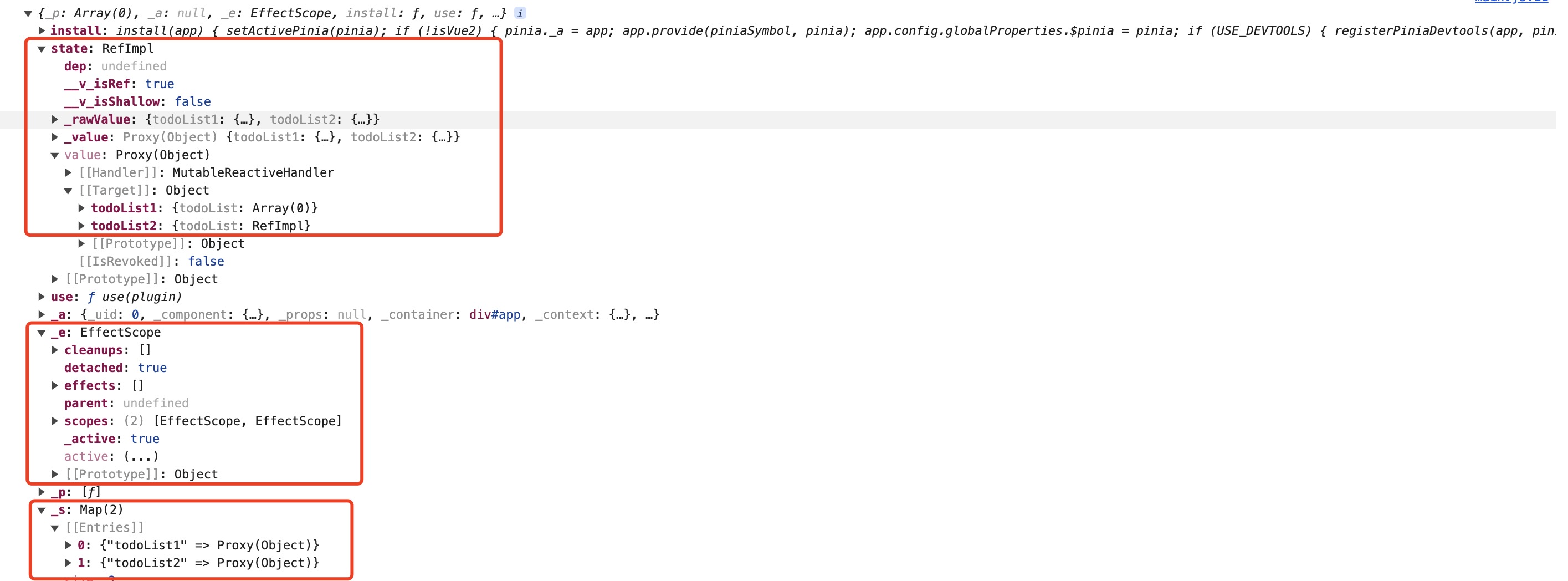
.mount('#app');注意 createPinia 的返回到底是什么

- install: 注册函数。
- use: install 阶段之前的插件保存在 toBeInstalled 中, install 的过程中会将 toBeInstalled 转移到 _p 中。
- _p: 插件集合
- _a: 当前 Vue 实例
- _e: effectScope 副作用空间,用于存储所有 store 的副作用函数 (getters),并且每个 store 会在 _e 中单独声明,方便统一管理(销毁等)
- _s: map 数据结构,保存所有 store,store 的 id 作为 key; 实例为 value; 存储每个 store
- state: 保存所有的 store 数据,store 的 id 作为 key; state 为 value; 用于存储 store 的所有可访问变量。
counter options demo
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
export const useCounter1 = defineStore('counter1', {
state: () => ({
count: []
}),
getters: {
doubleCount: state => state.count * 2,
},
actions: {
increment() {
this.state.count++
}
}
})counter setup demo
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
export const useCounter2 = defineStore('counter2', () => {
const count = ref(0);
const doubleCount = computed(() => count * 2);
const increment = () => count.value += 1;
return {
count, doubleCount, increment
}
});使用
import { useCounter1 } from './store/counter1';
import { useCounter2 } from './store/counter2';
const { counter: counter1 } = useCounter1();
const { counter: counter2 } = useCounter2();使用之后可以看出在实例的 _e, _s, state 中已经存在了对应的数据, 也就是说只有当用户 use 的时候数据才会被填充进 store 中
counter 视图 demo
<template>
<button @click="increment">{{ store.count }}</button>
<span style="padding-left: 10px">{{ store.doubleCount }}</span>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue';
import { useCounter1 } from '../store/counter1';
const store = useCounter1();
const { increment } = useCounter1();
</script>